Hannah Harkes is an artist who works in two, three, and four dimensions.
input
input
The following are notes from the Death Art & Anatomy conference at the University of Winchester (05062016)
ROBERTA FUSCO: PUTRIDAIRA (STRAINER ROOM) AND DRAINING PRACTICES OF THE BODIES. ANTHROPOLOGY OF DEATH IN THE MODERN AGE

ROBERTA BALLESTRIERO: FROM THE 'PLAGUE' TO THE 'VANITY OF THE HUMAN GLORY': THE "THEATRES OF DEATH" OF GAETANO GIULIO ZUMBO
18th cent. the plague. collector of victims, white bandage, smell, ant'infection. 1630 plague in milano. mattia preti - plague in naples (mirror image - mother and monato). domenzio gargiulo piazza mecerrello duratela peste del. laca giordono - san gennard frees naples. nicholas poussin the plague at atoing. original images traveled freely, quickly. marcantono roimodi Il Morbetto (after raphael, 16th cent.) 2nd theatre - the triumph of time. vivid livid tone of skin (red is only living body) human anatomy is quite convincing. portrait of zumbo next to red foot.
 .
.input
The following are notes from the Death Art & Anatomy conference at the University of Winchester (04062016)
PANEL B
CAROLINE DIEZYN - "TO TELL THE TODUS THEROPON WITH TUNG WERE FUL TERE"
Toads - simple momento mori to comment on luxuria.
In this paper - double tiered transi tombs, only.
Francois de la Sarraz in Switzerland (late 14th cent.)

12th century writers - body as food for worms.
The Awntyrs off Arthur.
Frogs on mouth, eyes, genitals - rather than spontaneous generation of worms, toads, etc, these were intentional placed to show nature of sins.
Question: genitals or abdomen? ie lust or gluttony?
Worms represented repentance, frogs the sins themselves.
poem (?) - dream vision, dialogue between body and worms. "Greens" greenery + vigour/desire.
Toads - luxuria - terra figure - classical to carolinia - snake mother - sins of flesh - corpulent full breasted - woman/sexuality=carnality - in the 12th century she transformed into luxuria - children (?), breasts more obvious - snakes were first companions, then nurslings, then biting her breasts.
11th cent. manuscript, demon drips her pointed shoes, man pulling up garments approaches from left - toad leaping at her from devil's mouth, revelations.
Monk from st. vicker - perturema
amntyrs off arthur - "ghost"? or corporeal form coming back to life (ie transi resurrection)
luxuria transis are not a franciscan message (give away your wealth) rather, "wear a hairshirt".
but there is more happening when reptiles are involved.
Matthias Grünewald 1434-1494, Flemish Painter of the Gothic Era. The Dead Lovers
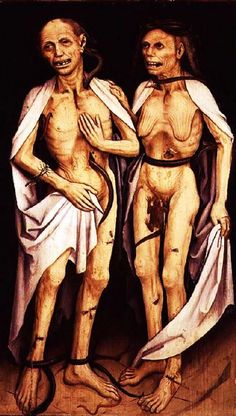
skeleton is not gendered. different hats suggest gender & class.
ELLIE PRIDGEON: CONSIDERING CADAVERS IN MEDIEVAL AND POST-REFORMATION WALL PAINTING
Psalter of Robert de Lisle, british library, MS Arundel 83 (c.1310).
3 living, 3 dead, 14th cent. in particular.
located in the nave, so deity had access.
Tarrant Crawford, Dorset (early 14th cent.) - high status paintings.
S shaped sway is common.
Hurstbourne Tarrant Hampshire, 3+3, (14th cent.) again in nave (north aisle).
salisbury cathedral gough map 32 bodleirs library, oxford, refurbishment in 18th cent. hungerford chapel at east end of cathedral.
illustrations of Hungerford Chapel interior in Gough R, Sepulchral monuments (1796). Lady Margaret Hungerford, Robert Lord Hungerford monuments. Near doorway so family saw them, walking in and out.
Death and the Gallant, Gough Map 32, Bodlein Library (late a8th cent.) - "Graceless gallant" ie well dressed, lust and price, "to the dead bodies, cast down thine eye".
Death and Gallant, Llancarfan, Wales, late 15th cent. nave. Death pulls gallant round corner to look at grave. warning image regarding behaviour.

"churches were whitewashed after the reformation and to this day," say people. - NOT TRUE.
Apostles- Creed, Harlington, Derbyshire.
Ten commandments, Ashby st ledgers, northamptonshire.
position of post-ref wall painting (as with medieval) mainly nave, north aisle, south aisle.
'Death', Ashby St Ledgers, Northamptonshire.

By 18th cent., figure painting in churches was more acceptable.
18th cent. death has anvil/hammer + spade for digging graves.
Death, Patricio, Wales, 18th.

Death, Dore Abbey, Herefordshire, early 18th, high status.
Father Time, Dore Abbey. Scythe, hour glass.

Maybe from Rubens Cronus Devouring His Children (1637-38). Anyway out of the classical world.

Old Father Time, Ashby st ledgers, Northamptonshire, 18th cent. Scythe is only reason to know it is father time from 18th cent.
CONCLUSION: Nave location/function of space. Eventual re-adoption of cadaver imagery long after reformation. Medieval cadaver paintings function as warnings regarding earthly pursuits and morality (death and the gallant) but this is NOT SO in reformation which is more about reminding (but not morally) that life is passing - just have to wait for hour glass.
Death (Dore Abbey) is high status - know because spinal column + 2 bones in arm shows anatomical knowledge.
High status known through colour palette - earthy pigments in both types of paintings, low key. Higher status = brighter, weather better, greater range. In medieval + renaissance, pigments are requested in specifics (imported from Afghanistan?).
IVAN CENZI: CADAVER MIRABILIS: ROME'S CAPUCHIN CRYPT AND THE BRIGHT SIDE OF MOMENTO MORI

In italy, direct contact between dead and living is possible.
Chiesa di Santa Maria Immaculates.
1626-1631
17th cent. But medieval influence.
Decoration of crypt 1732-1775.
Marquis de Sade escaping sex scandals, visited crypt and left description.
4000 friars buried here.
הֲבֵל הֲבָלִים הַכֹּל הָבֶל
havel havalim, hakol havel (4th/3rd cent. BCE).
All actions rendered “havel” ie futile, by death.
Eclasiasus most scandalous book.
-Lacked faith in goodness of god's creation.
-Death devoids life of all meaning.
-Evolved into effort to place goodness in afterlife.
-Le Gulf pointing out talking about physical body.
-Changing of wind.
Horatic's Carpe Diem as opposite of Momento Mori.
3 living, 3 dead – first as iconic or literary? Literature: 5 french, 3 german, 1 italian, 1 dutch at same time as artistic (visual) representations were appearing.
Late 13th cent. In engravings, stained glass.
Predates Dans Macabre (or Dans Macabre predates?) by 1 cent.
Origin might have been Lindt + cult of the Maccabees.
"The Martyrdom of the Seven Maccabees" by Antonio Ciseri (1800s)

Maccabees -> proto martyrs.
Macabre -> Maccabees
Dans – all stood in circle and one by one left circle to consider Maccabees.
4th book of Maccabees (not in the greek bible) bros described as doing a dance to exorcise fear of death and torture.
Death & the Maiden – vanity gains modern meaning.
Triumph of death – allegory of plague.
3 ages of (wo)man + 3 stages of corpse.
Leyanasula – life is frail like soap bubble.
Et in Arcadia Ego = even I was in arcadia (utopic land). Either dead man speaking from grave OR death is even present in arcadia, too (ie death speaking).
Intersecting medical, science, religion, art.
Wax figure from 17th cent. -> anatomical __(?) “Jesus was a man down to internal organs.”
”The Good Death” at beginning (?)
St. Francis thanks lord for all. When death comes, he sees death as his sister.
Canticle or the creature 1224.
1. Death of body. 2. Damnation of soul.
6 CHAMBERS. (7th grey is bookshop).
Scatological journey.
Journey up through human body (as journey through chambers).
1st CHAMBER

Quantity of bones arranged. Focus is 3 small skeletons (as the only 3 assembled) – young princess + 2 young brothers.
”Death has no age limit”.
Winged hour glass = “time flies”.
Medieval = that which you are we were what we are you will be ie 3 dead.
On the ceiling – scythe + scales enclosed by almost shape (fish bladder) polysenic symbol: “glory of god” + embyro in womb. Death as seed in womb = we start dying as soon as we are born / death is seed of new life (Franciscan, death's door).
2nd CHAMBER (tibias + femurs, leg crypt).

Burial ground underneath, bones arranged... space was tight. Franciscan coat of arms.
3rd CHAMBER (pelvis crypt).

Mummification (catacomb of polemo is the largest collection of mummies, around 12000).
4th CHAMBER (skull crypt).

Symbol of universe.
Last spinal bone 'Atlas', greek god, holding up earth.
Good equaliser.
Actors lower their masks.
Theatrical display.
5th CHAMBER (penance).
Chapel for mass, penance. No bones. Painting of holy mary.
6th CHAMBER (resurrection crypt).
Hope. 3 theological virtues.
DECORATIVE.
Clocks = fleeting time / eternity.
Cross.
7 point star = virgin, holy mary.
Winged hourglass (time flies.)
Winged skull (might seem like macabre version of angel but NOT, rather triumph of soul over body. Soul flying towards absolute or salvation.)
Bones are not only friars' but transfixed, transfigured, symbols representing “all”. What is beautiful, must be great.
Chapel makes death worthy of being admired. Striking to modern sensibilities. Death is not only accepted but admired.
Almost shape – tarot card – the world (garland) – accomplishment and finality – mostly around figure of christ – SEED.
Owners of bones? Cabitchen friars only. They could not be buried in same ground as seculars (aside from 1 exception – niece of pope whose mummified heart is in the penance (5th) chamber.
Public was allowed in (for prayers and mass), at least those devoted to the order had access.
Side chapels? From right nave of church, descent into crypt nut not thought of as on the itinerary.
Mummies in crypt – technique? After spontaneous mummification , friars developed method, specially formed(?) corpses, and drained (seated or in other positions). Central / southern italy. Bodily fluids drain for 8 months to a year. Then cleanse, aroma, dry in sun, close orifices with straw or other.
CAROL RAWCLIFFE: DEATH IN THE LATE MEDIEVAL HOSPITAL
Leprosy.
John Guy – exasperation about hospital historians “Guards van rather than van guard.”
Over 1300 medieval English hospitals.
Sick, elderly, disabled, poor (unlike today).
Norwich, St Giles (unesco hospital archive) around 60 patients.
Hospitals, like monasteries, so disappear at reformation.
St Leonard's, York, 200+ patients.
St Mary Bishop's, destroyed at reformation. Small leper hospitals (stewbridge, cambridge), pilgrim hospitals, after black death – alms houses (care for elderly first issue).
Most were religious institutions (so vulnerable to protestant reform).
Rich man camel needle.
17th canto divine comedy dante – serpent tail.
Dives Nazareth. Luke 16. colours. Nazareth at door. Dives sets dogs on him -> goes to heaven. “Rich man no pity of poor folk.”
feed, water, clothe, visit prisoners (lepers are prisoners in their own bodies)/sick, receive homeless, bury dead.
1st requirement in medieval hospital = confession (particularly urgent after black death).
Hospitals caught between rising wages and falling rates.
Growing desire for funerary spectacle.
”celestial capital”.
Cartesian volume – ascent from purgatory / celestial bucket.
Richard Wittington – financer – loans to crown. 3 x mayor of London – alms house, principle concern: state of soul. Wittington on deathbed (drawing?) Too late for medicine, glass in background, when urine is black yer a goner. Poor praying Witt's soul out of purgatory.
Bart's hospital in Smithfield.
Window depicting 7 comfortable works. Gatehouse bares patrons' coat of arms. Who do you pray for?”
Durham hospital – heraldic arms of Bishop Burry + Edward Howard <-- poor not to forget who they must pray for.
Savoy hospital, Henry 7th. “A view of the Savoy from the River Thames” (drawing?) Tudor roses. Coat of arms even on bedspreads!
St Cross in Winchester (Beaufort's) kneeling beside v. Mary, completed 1446. Had full confidence in hierarchies of this world + influence on next.
Humbleness/pride. Give wealth to poor / advertise.
Donors could even be not very rich. Just a little was enough for their name to be written in the “book of the dead” - Morte legium – which was held up beside the chapel during mass. Entry originally says “Prayers in vitae and morte”, after death, “vita” is crossed out.
Scatological.
High les garsh.... Lübeck. Jesus in an almond in the middle, patrons in circles surrounding, so it's clear in mass who to pray for.
Queen Elizabeth's reign – forbid idolatry. Commemorative institutions not much liked by protestants.
Alice transi. When praying, transi was visible because kneeling.
Many wanted to be close to the mass after death.
Priest with initials (HP) on the back of his coat, so that as he turned to face the alter, back to the congregation, the initials were clear to him.
Symbolic proximity to christ + it impresses the congregation.
Sacraments (of all, mass was most important).
Norwich – investment in hereafter.
Bishop Goldwell's arms next to personal chantry. Bishop in the dance of death in stained glass. When the protestants smashed up the place, they left behind this 1 panel untouched because it showed a catholic being taken away by death.
St Mary's in Winchester – 8 places were reserved for patron's servants. Don't want any old riff raff poor praying for you.
The idea of leprosy as unclean came with the victorians.
Christ looked like and loved the leper. Lepers go straight to heaven, so they're particularly blessed (that is, leper prayer is high quality prayer, but only if we're talking a devout leper.)
Grunwald crucifixion. St Augustine christus medicus.
Hospitals function often changed quickly – leprosarium, school, alms, hospital...
Medieval hospitals didn't cure, there was almost no medical staff working (none in england). Main treatment focused on air, diet, cleanliness, passion of the soul: music, all the time in St. Giles. Management of disease. Healthy environment. They wouldn't take the wounded – blood was sacrilegious. Wouldn't take those with infectious diseases. Again, holistic nature of medieval medicine. Prevention (through healthy diet etc) rather than cure. If the patient prayed, they were more likely to get better because they would not be anxious.
The charitable institution also buried its dead. It was a privilege to die in hospital, in the arms of the church. In those days, it was not a failure when the patient died, as it is now. Patient was given cross to hold.
The medieval believed disease to be spread on “corrupt air”.
The mind worked on a balance of the humours.
Some hospitals were attacked in the peasant revolt. (They were a waste of money, spending on patrons rather than patients).
PANEL C
JAMES HALL: THE RENAISSANCE ARTIST AS ANATOMIST: BANDINELLI, MICHELANGELO AND THE VOGUE FOR CREATIVE DESTRUCTION
Bandinelli, Self Portrait (1528-30).
Dissecting sculptor shows power over life and death + understands body.
Picasso – every act of creation is first an act of destruction.
Bandinelli first to accord demi-urgic powers.
Bandinelli's Self Portrait (1544). Colossus. In this one he became male not female, aggressive not tranquil, Michaelangelo not...

Grasping Hercules' head. He is an upgraded Hercules. Iconoclast? Creator? Dissatisfied sculptor?
Donatello Sacrifice of Isaac from Cathedral Bell Tower.
Holbein Erasmus with Terminus (c.1520-25).
Bandinelli Self Portrait (1548), hemmed in on all sides. Time has destroyed and is destroying antique sculpture but BB will recreate!
Rise of anatomical dissection BUT remained controversial into the 16th cent. Some said “Barbaric, unchristian!” others that it “revealed wonders of god's creation”.
Michelangelo compares himself often to weapons in his poetry. Bent Syrian bow, physical hardship, shoots through crooked barrel, explodes like a canon...
Leonardo's riddle - “Alas, I see the saviour crucified once more!” Solution – sculptor carving crucifix.
Francesco Salviati Portrait of a Goldsmith (1528).
Pathos in anatomical study.
17-18th cent. artist, creator/destroyer.
Artist posing with antique head fragment, head in pain. Shows respect for antique but also expressive progression (Van Dych Iconologia 1520s). Distressed female head most popular.
Superiority over classics. yeah.
TERESA LOUSA: WHAT ABOUT CORPSE AS ARTISTIC RESOURCE?
Andres Serrano. Teresa Margulles (tongue). Is corpse as art one of last taboos left? Pushing boundaries? Teresa Lousa thinks “Yes”.
NIGEL LLEWELLYN: BRONZE BODIES
(Introduced by Maya Warrior – head of theology, religion, philosophy).
West Hill Cemetery, Winchester. A team including Tina are mapping the cemetery.
Event – Death In Scotland (January).
Medieval effigies with crossed feet = crusades.
Thanotology? Rather 'Death Studies'.
Intolerance to accept existing boundaries.
Old way = death as moment. No. Medical science disconnects moment, makes period.
We cannot separate body from art.
Thinking about links between then & now, universality, be careful!! Can trigger responses...
Need big framing ideas. TIME. Social science. Rejects life/death binary, rather “dying”. Anthropologists. Length of timeline, timeline approach helps more than binary does (individuals + cultures). Ritual needed.
Reformation ->1660 1/3rd of effigies are erected in lifetime of person commemorated.
Ancestors habitually erect monument to themselves. Time is frozen. 17 years between erection and death.
Leaving resources for chantry prayers but also funds for prayers during lifetime!
Art of Death at V and A. 20 years ago.
Monuments – starting point – function = monumental body. It fills a space left by death. Natural, social, (monumental) body. Cantorovitz split. “The King Is Dead.” “Long Live The King.” (ie natural body, social or political body.... successor lives).
What the person represents continues. Monuments are works of art which express what will be continues by the monument.
When looking at effigies, Nigel looks at 4 kinds of content: - sculpted body (effigial, subsidiary, allegorical); - architectural framing (canopies over chantries; - inscribed word; - heraldry.
THE WESTON MONUMENT.
Laudianism = kickback to puritan; dignity, procession, display; clergy separate, looked up to; “higher church”; vestments brought back; images SANCTIONED (2nd commandment but if didactic then they're fine).
But this was not done tastefully. I was hated in the 1830s because of the gothic revival. “The liberality if not the taste of a fox!”.
.........................................and so on............................
Talking at lunch with Romany – Agency of tree/stone grave ie agency of stillness. (X)LOOK UP – Arno Vale ... something... in a graveyard; trees and hybrid geographies, dwelling, monitoring and resistance in Bristol Cemetery. Paul Cloke + Owen Jones.
.The following are notes from the Death Art & Anatomy conference at the University of Winchester (03062016)
input
Invited speaker PAMELA KING: Cadaver tombs - whose choice?
Rejected Hegelian model. Looked at cadavers in terms of : - geographical location - social network - iconography
The fashion for shrouds moved outwards and socially downwards.
Momento mori - Did cadaver tombs serve an education purpose? King suggests - "no"
Many variations in iconography - (point of death or of decay? double tiered or single? standing, recumbent or kneeling? personification of general death figure or of the individual *interesting point that this distinction is not made in wills*, real or allegorical ie state of sin? horror and fear or comfort of release?)
Henry Chichele - Duchy of Lancastar estate, perhaps wished for release in 1427, following a conflict between Henry Beaufort and pope, who retaliated by appointing a 16 year old italian as Chicele's archdeacon.
Did he chose the cadaver tomb out of nostalgia for Canterbury Cathedral?
John Colet - border between asceticism and humanism. Erasmus sought him out, then claimed christ had a natural fear of death.
John (de) la grange in Avignon - 5 joys of the virgin - dans macabre OR was it satirical? is customised politically, rather than religiously?
Ralph Woodfor 1428 - cadaver inscribed slab. Surface orthodox piety to cover the deeply personal. His tomb was not in his will, so was it already in place? He appeared in his will to be pedantic, anxious, even counting cattle. Ralph stretched the decorum and formula of the medieval will - why? Because he was disinherited because of the woman he married, who died? The will AND tomb suggest an anxious individual (due to the background war of the roses / family dispute?)
Isabel (le) Dispenser - in her descriptive wishes for her tomb, she was buying shoes!
Edward 4th asked for a cadaver tomb but did not get one... but where did he get the idea?
Often the cadaver tomb was not the idea of the dead - look at Thomas and Agnes who had 21 children and were represent in shroud bundles, with tied feet. Was this because they died so many years (a century) before the tomb was made that no one had their portrait or an idea of how they looked? Was it because they were very dead?
John Fitz Allen (?) died at 28 years old - did he consider his tomb? Folk Atum (?) brought his boned back and died with a will claiming the debt he was owed for bone return. There must have been an agreement made between Fitz Allen & Atum families, as the tomb was made. He was related to Dispenser /Beechem(?) family.
York Ministery - Haxey's/Haxies tomb (the man who commissioned it was not the dead man - but friend? Showing affections between celibate men?
Elizabeth Tame
How often do we choose our own memorial? How often is it chosen by grieving families in a state of shock?
Roger Rockley (d. 1553) Was it fashion, political affiliation, social position? Why choose a cadaver tomb?
John Donne posed in his shroud
In Scotland? Kirkwell in Orkney - 18th century.
Are there children involved? Yes, on brasses. The parents are shrouded or not and the children appear as small figures underneath, the dead shrouded, the others not. Stillbirths appear in swaddling clothes.
Chicele 1427 - However much pomp in life, you will come to this. The office is a burden, there is release in death.
Le Grange - dans macabre supra-structure/superstructure
PANEL A - Art, Death & Disease
Fiona Davis
Deleuze - between life and death, is life playing with death?
Geometry - point has no physical dimension (so death must be a period, rather than a point)
"Cruel Optimism" - slow death - Lauren.... (obesity)
Chronic time - David Morris - Endurance performance art - Disruption of temporal (of chronic disease)
FRANCESCO MARIO CALASSI - Morphology & Pathology of the Temporary Artery in artistic representations
Ethical point - there must be a scientific question before exhuming a body, it can't be done just out of the spirit of adventure.
Julius Caesar - did he have a stroke or epilepsy?
How much is anachronism? To challenge that concern we must combine philology, art and medicine.
The Italian Paleopathography Project
Renaissance art - Teofilo Fulengo (poet) - Facial paralysis - central not peripheral

Superficial temporal artery, "Here death is bled to be able to help life" (?)
Horton's disease
The question is, "How ancient is temporal arteritis?" - Appelboom; van Eigem
1350BC the tomb of Pa-Atom-Em-Heb who appears in stone carving as "blind harpist". Did he suffer from temporal arteritis?

Renaissance Flemish Italians were very particular about detail. Canon Van der Peale by Jan Van Eyck shows scar formation and loss of hair from the eyebrow and in front of the ear.

Writing from the time states Canon found difficulties attending morning service and by the time of the portrait painting, he was forced to stay at home - signs of temporal arteritis
Ritratto di comes anziano (1485) Florene
Ambroise Pare (1510-1590) - migraines, bloodletting
Ferrante 1 of Aragon (1431-1494) king of Naples. Lamentation of Guido Mazzani.
Francesco Giamberti (1405-1480) by Piere de Cosime - diagnosed by 4 physicians in current day
Filippino Lippi's (1419-1504) Saint Frediano - paper written by Francesco Mario Galassi
Andrea Mantegna - Profile d'uomo (1448-1450)
Poloi Pezzoli - had no social problem painting realistically rickets, dwarfism
Flemish painters' understanding of rheumatological conditions.
What's the NEXT STEP? - reasses literature - paleopathological study (exhumation of the body) ---> genetics of temporal arteritis.
"BUUTT! Edwin Smith Papyrus?" says audience
Must first get bodily evidence and with that, reflect back upon the cultural objects (texts, paintings) but both images and words cannot be read from a modern perspective as evidence
EMILY POORE
depiction of syphilis in woodcuts
Dürer's Syphilitic Man (1496)

Secular and religious imagery / causal explanation
Symptoms, individual case, all shown (who why what when where)
French Troops and Artillery Entering Naples in 1495 (c.1498)

prostitutes - neapolitans expelled charles + soldiers
Alexanrei Benedicti - description of syphilis
Evan Block - 18 pages of synonyms for syphilis (ie countries trying to blame each other)
Head of a Prostitute with End-Stage Syphilitic Rhinitis (1790), engraving, vienna

Sebastian Brant woodcut (1496) De pestilentiali scorra, sive

Physicians of body acknowledged god but focused on physical explanations
Josephus Grünpeck - De pestilentiali scorra, sive Mala de Franzos. [Augsburg: Johann Schaur, between 18 Oct. & 17 Dec. 1496.]

Pestblätter - pamphlets (early renaissance)
Dürer Self Portrait (1493)
"give my compliments to our friar... nothing of which I am more badly afraid..."... than syphilis (letter telling how Dürer was afraid of S

Celestial diagrams / zodiac man - Johannes de Ketham (1493) Festiculo de Medicina
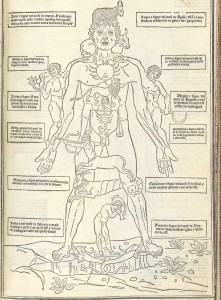
Conjuntion of 4 (heavenly bodies in alignment) + sign of scorpio. Apollo, dream, responsible for outbreak.
The Doctrine of the Four Humours
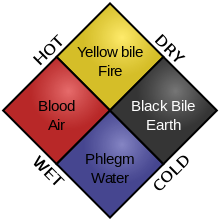
Coat of arms - city where authorised reports of syphilis. Sun motif at bottom - apollo (dreamt outbreak planetary reason)
Importance of dress (of D's syphilitic man) for identity - LANDSKNECHT
Five Landsknechte and an Oriental on Horseback - Dürer (1495-1496)

It was more lucrative to be a soldier than to work in agriculture. Many soldiers were paid in cloth. Landsknechte were in fact impoverished peasants, contrary to what rich clothing suggests. They supported enemies of their own country, bought prostitutes...
Hans Knapp Lansknecht (c.1511) (?)
Urs Graf Two Mercenaries, Whore and Death (1524)

I am surprised there is no money in the land (günsberg?) 1524
~1520 the connection between syphilis and sex was accepted (until then it was a combination of the sexual and the celestial)
plural view of late 16th century medicine
D's Syphilitic man has arms outstretched in the ostentatio vulnerum gesture
Man of Sorrows (c.1465-1470)
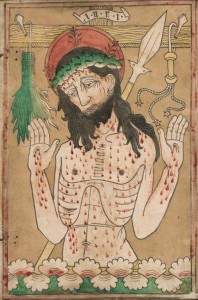
in this image, christ is simultaneously alive and dead
"andachtsbilder" - image for pious meditation
Was D's S man a selfless sacrifice or punishment for indulgence? as with christ's wounds - ongoing chronic illness.
St. Brocks & St. Sebastian were evoked because of a similarity in bodily marks
REFRESHMENTS (X)LOOK UP - Elina Gertsman - Estonia - Dans Macabre (?)
POETRY - Richard Barnett - Bog Bodies
Worcestershire - Geofrey hill, Elgar, Houseman
Henry James gradations
.input
I am NOT sitting in a room, solo exhibition by Taavi Suisalu.
Performance by Erik Alalooga.
Supersonicum , koidu seltsimaja, jakobsoni 18, viljandi



 + breakfast with elvar, tea, heino eerme .
+ breakfast with elvar, tea, heino eerme .input
Joachim Kahl - The Misery of Christianity
Richard Phillips - Mapping Men and Empire: A Geography of Adventure
.inprogress
kevadnäitus avamine, tallinna kunstihoones (agryfp-ega) Комикс "Это", линогравюра, 2015 (foto: Karel Koplimets) .
Комикс "Это", линогравюра, 2015 (foto: Karel Koplimets) .Copyright © 2024 | MH Purity lite WordPress Theme by MH Themes